Understanding Anxiety in Children
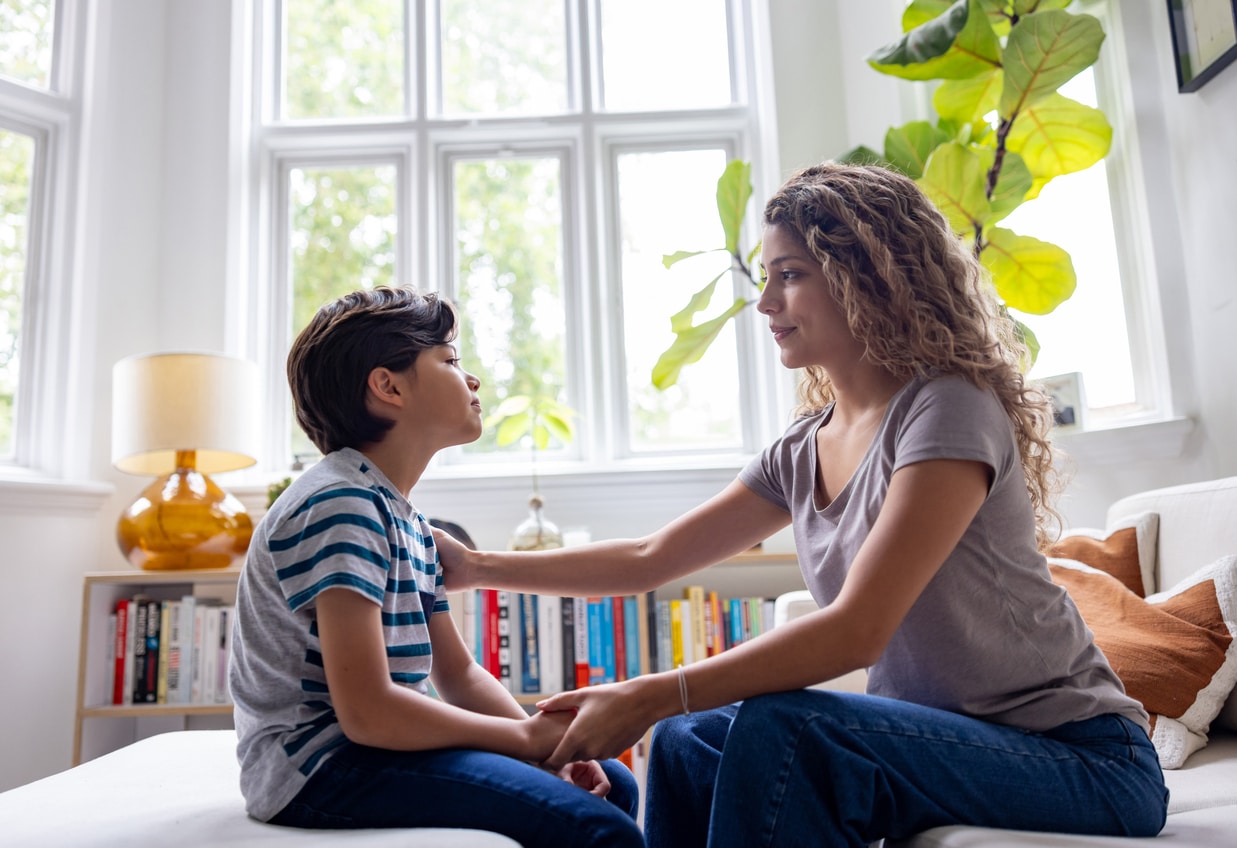

Anxiety, a natural part of growing up, can sometimes evolve into a challenging hurdle for children, impacting their daily lives and development. Recognizing the signs, triggers, and effects of anxiety in children is the first step in offering the vital assistance needed. As a parent or caregiver, it’s important to understand anxiety in children and the profound impact it can have on a child’s growth.
What is Anxiety in Children?
Anxiety in children is an emotional state characterized by feelings of unease, worry, and fear. It is a normal part of growing up and can help children develop the necessary tools to deal with challenging situations. However, when anxiety becomes chronic and excessive, it can negatively impact a child’s well-being.
Children may experience different types of anxiety, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, specific phobias, separation anxiety, and panic disorder. Generalized anxiety is a persistent and excessive worry about a variety of everyday problems, while social anxiety involves intense fear of social situations. Specific phobias are irrational fears of particular objects or situations, and separation anxiety occurs when children are excessively afraid of being away from their caregivers. Panic disorder involves sudden and intense bursts of fear or panic.
What Does Anxiety Look Like in Children?
Anxiety can manifest differently in children than in adults. Children may not always have the words to express their feelings, so anxiety often presents itself through behavioral, emotional, and physical symptoms, including:
- Avoidance of specific situations or places
- Frequent temper tantrums or meltdowns
- Clinging to parents or caregivers
- Excessive reassurance-seeking behavior
- Excessive worry or fear about various issues
- Irritability and mood swings
- Perfectionism and self-criticism
- Muscle tension
- Rapid heartbeat
Common Causes of Anxiety in Children
Anxiety in children can stem from a variety of sources, and it’s often the result of a combination of factors. Some common causes of anxiety in children include:
- Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders can increase a child’s risk of developing anxiety.
- Brain Chemistry: Neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and dopamine, play a role in regulating mood and anxiety. Imbalances in these chemicals can contribute to anxiety.
- Environmental Stressors: Stressful life events, such as divorce, moving, or the death of a loved one, can trigger anxiety in children.
- Trauma: Exposure to traumatic events, such as accidents or abuse, can lead to anxiety.
- Parenting Style: Overprotective or controlling parenting styles can foster anxiety in children. On the other hand, inconsistent or neglectful parenting can also contribute to anxiety.
- Biological Factors: Physical conditions like thyroid disorders, allergies, and asthma can sometimes be linked to anxiety symptoms.
How Does Anxiety Affect Child Development?
Anxiety can have a profound impact on a child’s development. When left unaddressed, it can affect various aspects of their life:
- Social Development: Children with anxiety may struggle to make friends, engage in group activities, or interact with peers. Social anxiety can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Academic Performance: Anxiety can interfere with a child’s ability to concentrate, learn, and perform well in school. This can lead to academic struggles and decreased self-esteem.
- Emotional Well-being: Chronic anxiety can take a toll on a child’s emotional well-being, leading to low self-esteem, increased self-criticism, and a negative self-image.
- Physical Health: The physical symptoms of anxiety can affect a child’s overall health, leading to issues like sleep disturbances, headaches, and stomachaches.
- Long-term Impact: If not addressed, childhood anxiety can persist into adulthood, affecting a person’s overall quality of life.
Options for Anxiety Treatment for Children
If a child’s anxiety is severe or significantly interferes with their daily life, it may be necessary to seek professional help. Several treatment options are available for children with anxiety.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective and widely used therapies for treating anxiety in children. It focuses on helping children recognize and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with their anxiety. Through CBT, children learn valuable skills for managing their worries and fears.
Medication
In some cases, when anxiety is severe and significantly impairs a child’s daily functioning, a healthcare professional may recommend medication. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can help alleviate symptoms. Medication must be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare provider.
Art and Play Therapy
For younger children, art and play therapy can be an effective way to express and process their feelings and anxieties. Through creative activities, children can explore their emotions and fears in a safe and supportive environment.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Teaching children mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help them manage anxiety daily. Breathing exercises, guided imagery, and meditation can be valuable tools for reducing stress and promoting emotional well-being.